Your Alcohol and liver images are ready. Alcohol and liver are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Alcohol and liver files here. Download all free images.
If you’re searching for alcohol and liver images information linked to the alcohol and liver keyword, you have visit the ideal site. Our website frequently gives you suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Alcohol And Liver. The effects of alcohol on the liver depend on how much and how long you have been drinking. The symptoms of these three diseases may overlap. Your liver is a filter for everything you put in your body. Beverage alcohol (i.e., ethanol) is chiefly metabolized in the main parenchymal cells of the liver (i.e., hepatocytes) that make up about 70 percent of the liver mass.
 Alcohol Effects On The Body Gastrointestinal Disorders From steadyhealth.com
Alcohol Effects On The Body Gastrointestinal Disorders From steadyhealth.com
Excessive buildup of fat in the liver, also known as fatty liver or hepatic steatosis inflammation of the liver or alcoholic hepatitis 6 ingested alcohol is eliminated principally through its metabolic degradation. If you drink more than it can process, it can become seriously damaged. There are many health risks of chronic alcohol abuse, ranging from high blood pressure to stroke. The liver can develop new cells, but prolonged alcohol misuse (drinking too much) over many years can reduce its ability to regenerate. Since an individual’s susceptibility to the toxic effects of alcohol may vary by many factors including age, gender, genetics and coexistent medical conditions, it is reasonable for you to review alcohol use with your physician.
As alcohol continues to damage the liver, it will progress through fatty liver disease, alcoholic hepatitis, and finally, alcoholic cirrhosis.
There are four stages of alcohol induced liver disease. As alcohol continues to damage the liver, it will progress through fatty liver disease, alcoholic hepatitis, and finally, alcoholic cirrhosis. Drinking too much alcohol can lead to three stages of damage: Beverage alcohol (i.e., ethanol) is chiefly metabolized in the main parenchymal cells of the liver (i.e., hepatocytes) that make up about 70 percent of the liver mass. The liver can develop new cells, but prolonged alcohol misuse (drinking too much) over many years can reduce its ability to regenerate. The healthy liver structure is replaced with scars, causing the cells of the liver to die.
 Source: earthclinic.com
Source: earthclinic.com
People are most familiar with alcohol’s negative effects on the liver. Like everything else, moderation is key. Continuation of alcohol use will result in a higher risk of progression of liver disease and cirrhosis. Binge drinking or abusing alcohol over time can result in serious liver damage as it places a significant burden on the liver. Some additional signs of liver damage from alcohol are:
 Source: steadyhealth.com
Source: steadyhealth.com
Excessive buildup of fat in the liver, also known as fatty liver or hepatic steatosis inflammation of the liver or alcoholic hepatitis Your liver is a filter for everything you put in your body. This condition is irreversible, and the symptoms are similar to those of alcoholic hepatitis. Each time your liver filters alcohol, some of the liver cells die. Once the alcohol is in the bloodstream, it travels throughout the body effecting different tissues, like the brain.
 Source: steadyhealth.com
Source: steadyhealth.com
If you drink large amounts, your liver starts to have a hard time processing the alcohol. Drinking too much alcohol can lead to three stages of damage: Binge drinking or abusing alcohol over time can result in serious liver damage as it places a significant burden on the liver. Once the alcohol is in the bloodstream, it travels throughout the body effecting different tissues, like the brain. Heavy drinkers have an increased risk of jaundice, cirrhosis, liver failure, liver cancer, and many other conditions.
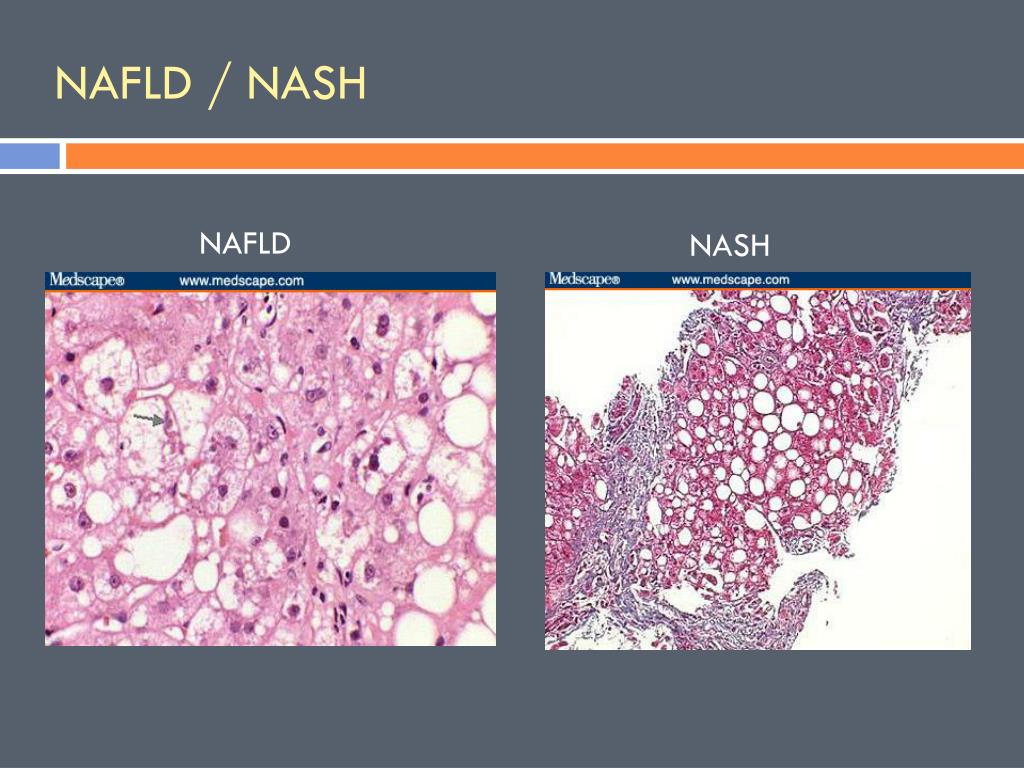 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Alcoholic liver disease is a result of overconsuming alcohol that damages the liver, leading to a buildup of fats, inflammation, and scarring. Over time, your liver can give out. Fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis and alcoholic cirrhosis, which can lead to liver failure and increases the risk of liver cancer. Beverage alcohol (i.e., ethanol) is chiefly metabolized in the main parenchymal cells of the liver (i.e., hepatocytes) that make up about 70 percent of the liver mass. Alcoholic liver disease is caused by heavy use of alcohol.
 Source: keeprecipes.com
Source: keeprecipes.com
Your liver is a filter for everything you put in your body. There are many health risks of chronic alcohol abuse, ranging from high blood pressure to stroke. Alcoholic liver disease is a common, but preventable, disease. Fatty liver, hepatitis and �scarring� of the liver. People are most familiar with alcohol’s negative effects on the liver.
 Source: mydr.com.au
Source: mydr.com.au
The effects of alcohol on the liver depend on how much and how long you have been drinking. Alcohol is a toxin and overconsumption taxes the liver. Over time, your liver can give out. Continuation of alcohol use will result in a higher risk of progression of liver disease and cirrhosis. Because alcohol is a toxin, your body tries to break it down and get rid of it.
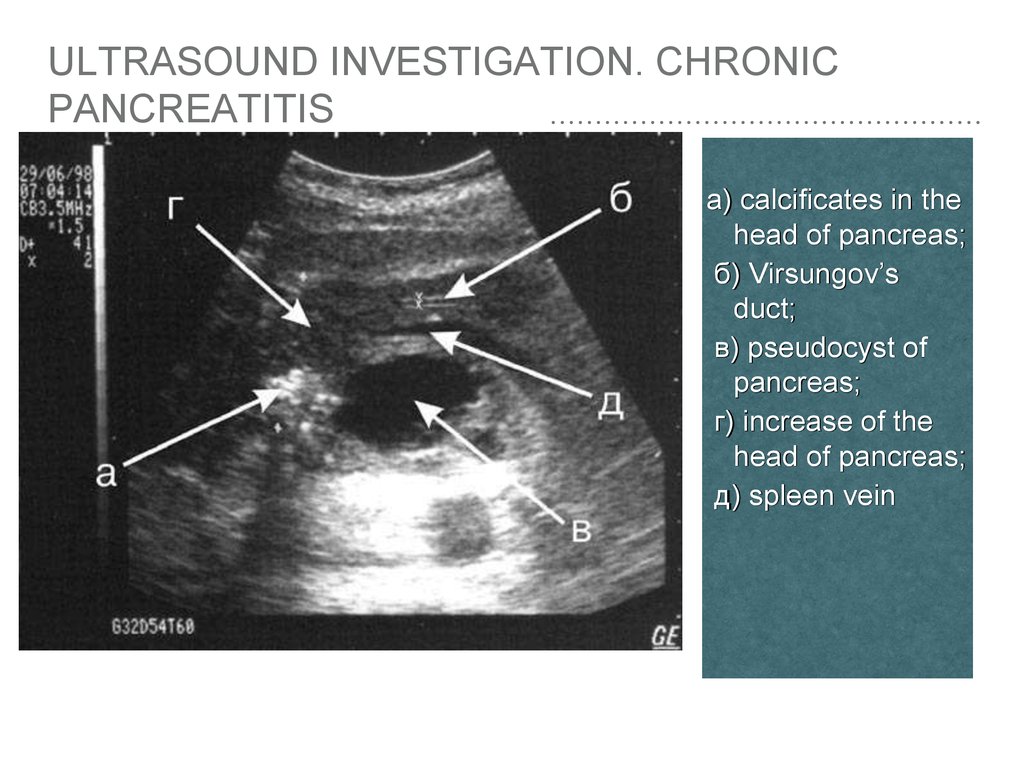 Source: en.ppt-online.org
Source: en.ppt-online.org
Each time your liver filters alcohol, some of the liver cells die. Clinical reports are difficult to interpret because insufficient attention has been given to the timing of alcohol intake in relation to the ingestion of paracetamol. People are most familiar with alcohol’s negative effects on the liver. If you drink large amounts, your liver starts to have a hard time processing the alcohol. Like everything else, moderation is key.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Like everything else, moderation is key. The alcohol moves directly from the stomach into the blood stream. Like everything else, moderation is key. Excessive buildup of fat in the liver, also known as fatty liver or hepatic steatosis inflammation of the liver or alcoholic hepatitis Continuation of alcohol use will result in a higher risk of progression of liver disease and cirrhosis.
 Source: research.qut.edu.au
Source: research.qut.edu.au
Alcoholic liver disease is caused by heavy use of alcohol. Some additional signs of liver damage from alcohol are: 6 ingested alcohol is eliminated principally through its metabolic degradation. Alcohol causes fat to accumulate in the liver, and this eventually can cause the liver to scar, which can lead to inflammation, as well as cirrhosis, fatty liver disease, and liver cancer. Excessive buildup of fat in the liver, also known as fatty liver or hepatic steatosis inflammation of the liver or alcoholic hepatitis
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title alcohol and liver by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





